Number Systems
What are Number Systems
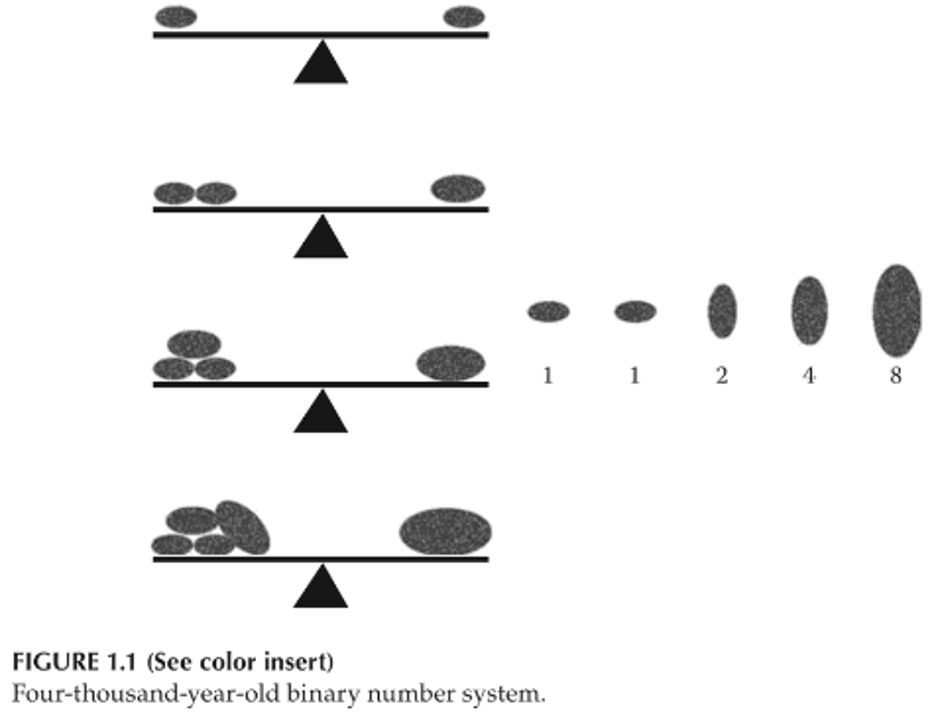
Ancient cultures developed a diverse range of numbering systems, but the most striking is the system developed by the Babylonians starting around 5,000 years ago. This system was a weighted positional system, using a base of 60 rather than the base 10 used in modern decimal systems. The Babylonians did not have a zero symbol, using a space instead. The influence of the number 60 is still seen in modern time and angle measurements. Additionally, binary concepts, often associated with modern computing, were used as early as 4,000 years ago for weighing stones with a balance (Dimitrov et al., 2017).
The ancient Romans used letters to represent their numbers, a system known as Roman numerals, which are often introduced to children. In this system, specific letters correspond to specific values: I represents 1, II represents 2, III represents 3, IV stands for 4 (with 1 placed before 5), V represents 5, X denotes 10, L signifies 50, C stands for 100, D represents 500, and M equals 1000. By combining these letters, larger integers can be formed. For example, the number 1998 is written as MCMXCVIII in Roman numerals (Kneusel, 2015).
The Romans built their numbers from earlier Egyptian numbers. Of course, we do not use either of these number systems for serious computation today for the simple reason that they are hard to work with (Kneusel, 2015).

A number system in mathematics is a well-defined system of representing, writing and expressing a numerical value which occurs in the measures of different dimensions and calculations. Numbers—the numeral values—are different for different types of computing system (Wahed, 2022). Number systems are very important to understand because the design and organization of a computer depends on the number systems (Dixit, 2005). When you input some letters, words, graphics, audio, video, etc., the computer translates them into its equivalent binary numbers (Bansal et al., 2017).
Whenever you will count anything, you will use numbers such as 1, 2, 3, etc. But a computer is a machine and it understands only machine language i.e. the language of 0's and l's. The computer does not understand human languages and whatever input is given to it is converted into machine language. Various number systems came into existence like octal number system and hexadecimal number system which uses the combination of digits to represent different quantities (Bansal et al., 2017).
The modern civilization is familiar with Decimal Number System, in which ten digits, namely 0 to 9 are used to represent any number. Once the famous Mathematician Laplace stated, "It is India that gave us the ingenious method of expressing all numbers by means of ten symbols, each symbol receiving a value of position as well as an absolute value, a profound and important idea which appears so simple to us now that we ignore its true merit." Thus, the importance of a number system does not lie in the number of symbols used in it but what is important in it is the concept of face value (absolute value) and the place value (value of position) of a symbol (Dixit, 2005). The value of each digit in a number depends on the following:
1. Face value of the digit: It represents the digits themselves like 1, 2, 5 and 6 in the number 1256.
2. Place value of the digit: It represents the units, tens, hundreds, thousands, etc.
Types of Number Systems
Understanding number systems is crucial for comprehending how computers work. Each system is designed for specific functions, including the representation and manipulation of data within computers (BYJU’S, n.d.). The useful number system types are:
1. Binary Number System
2. Octal Number System
3. Decimal Number System
4. Hexadecimal Number System (Dixit, 2005).
Binary Number System
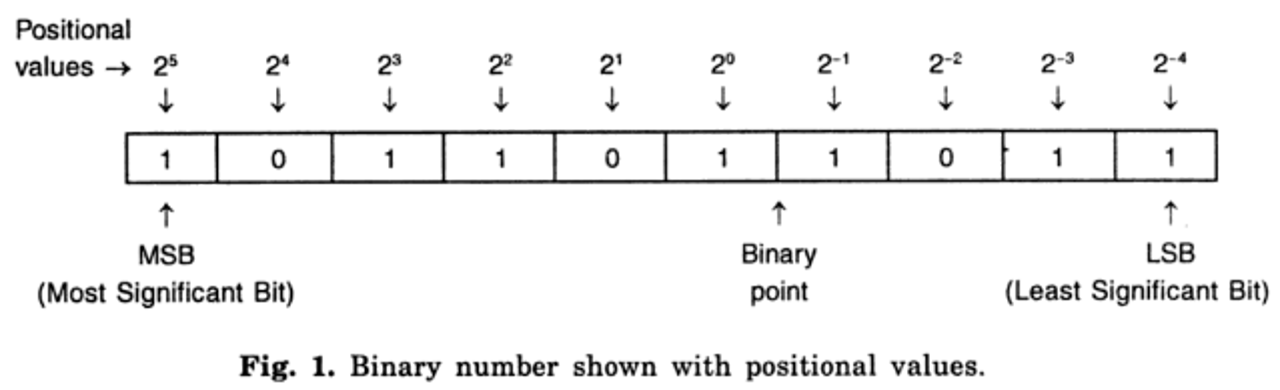
Binary is fundamental in computing, as it aligns with the on/off states of electronic circuits (GeeksforGeeks, 2020). The binary number system, as the name suggests, consists of two digits namely 0 and 1. These binary digits are called bits. Thus, the word bit stands for either of the binary digits. Since this system uses two digits only, it has the base or radix 2. In binary notation, each digit's positional value is twice that of the digit to its right, mirroring the structure of the decimal system but with a base of 2. Binary numbers are typically written with the base indicated as a subscript next to the least significant digit (LSD). For example,
(101101.1011)2
It can be represented as shown below (Dixit, 2005).
Octal Number System
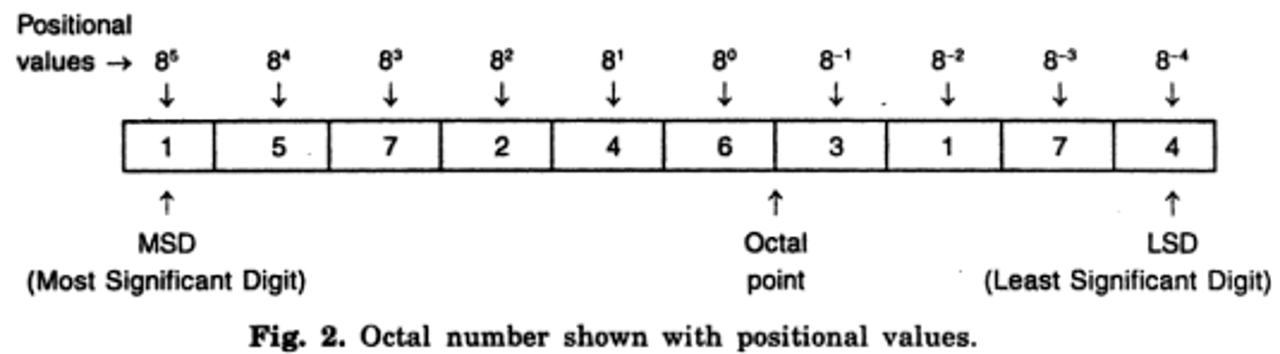
This number system has base or radix 8. The basic digits of this system are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7. In modern programming languages, octal numbers are typically reserved for character codes and will be rarely seen outside of that context (Kneusel, 2015). The octal number system is also a positional value system, wherein each octal digit has its own value or weight expressed as a power of 8. For example,
(157246.3174)8
It can be represented as shown below (Dixit, 2005).
Decimal Number System
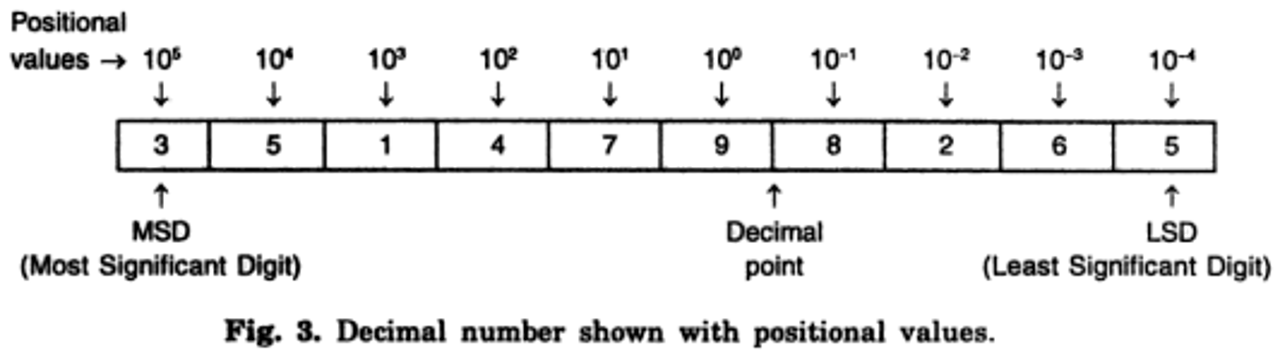
The decimal system is integral in everyday life and forms the basis for most mathematical calculations (Cuemath, n.d.). This system has roots in ancient civilizations, notably the Hindu-Arabic numeral system, which introduced the concept of zero and positional notation, significantly influencing mathematics and commerce (Britannica, 2024). The decimal number system uses ten digits (0 through 9) to represent numbers. Numbers such as 12876, -1024, 68.74, and +768 are examples of decimal numbers. The system also employs the decimal point and ± signs. The base or radix of the decimal system is 10, reflecting the number of digits used. In this system, while the base is 10, the fundamental digits are 0 through 9. The value of each digit in a decimal number depends on its face value, the base of the system, and its position within the number. For example,
351479.8265
It can be represented as shown below (Dixit, 2005).
Hexadecimal Number System
The hexadecimal number system, popularly known as the hex system, has sixteen symbols and therefore has the base or radix 16 or H. Hexadecimal is widely used in programming and computer science, particularly for memory addressing and color codes in web design (BYJU’S, n.d.). The hexadecimal number system represents an information in the concise form. The sixteen symbols used in this system are: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, and F.
The equivalence between hex-numbers and decimal numbers is given below:
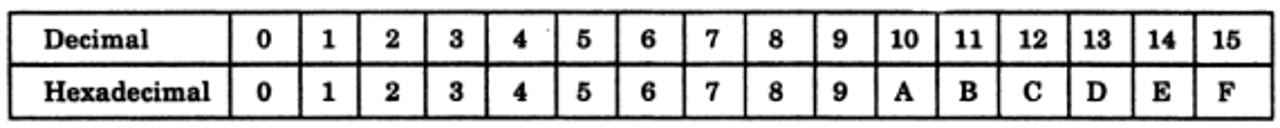
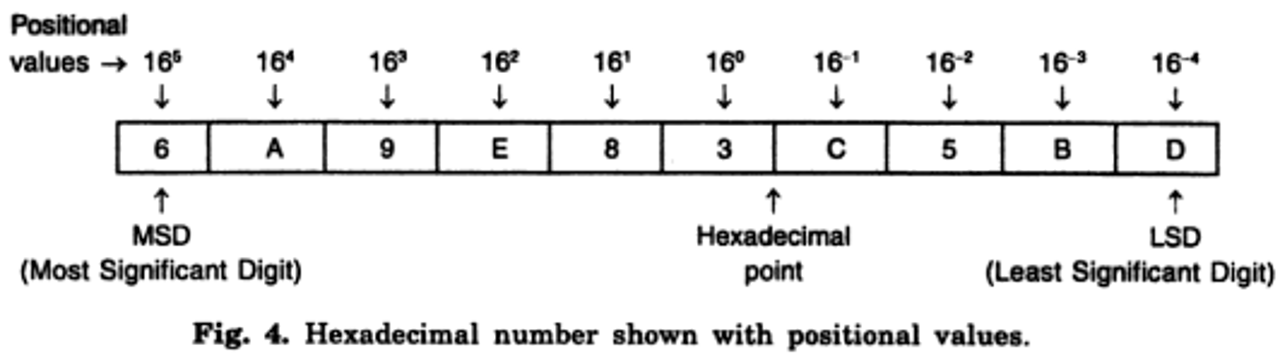
The hexadecimal number system is also a positional value system, wherein each hexadecimal digit/letter has its own value or weight expressed as a power of 16. For example,
(6A9E83.C5BD)16
It can be represented as shown below (Dixit, 2005).
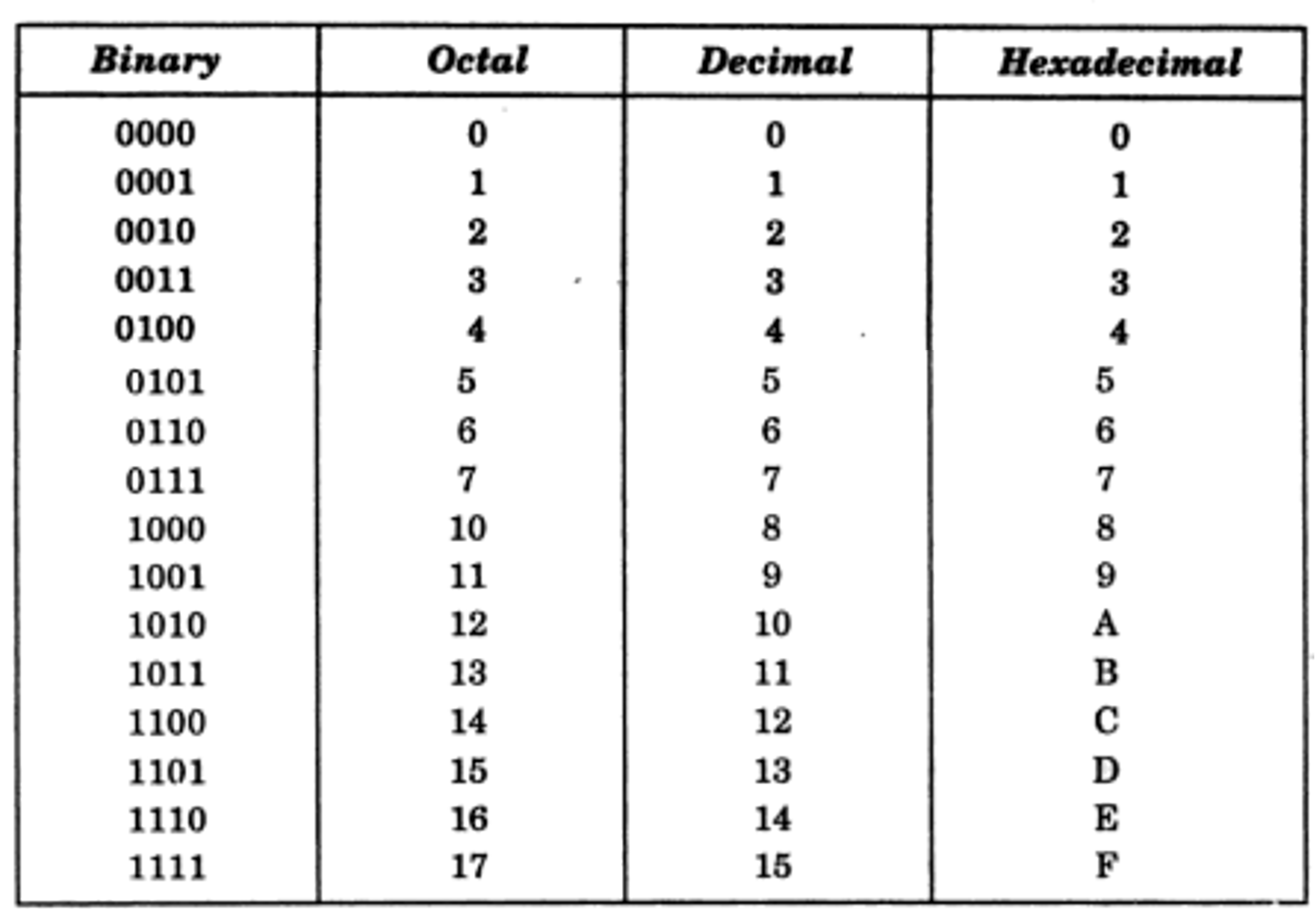
The following table illustrates the relationship between binary, octal, decimal, and hexadecimal number systems (Dixit, 2005).
Uses and Significance of Each Number System
Binary
Octal
Decimal
Hexadecimal
Analysis/Reaction
This portfolio dives into the world of number systems, a topic that might seem distant from our daily interactions with technology. But as a computer science student, I have come to realize just how crucial these systems are for the digital world we navigate. Four main number systems are highlighted: binary, octal, decimal (the one we use every day), and hexadecimal. While the decimal system reigns supreme for everyday tasks due to its alignment with the 10 digits of our hands, binary is the secret language of computers. Since computers operate on on/off switches, binary's use of just 0s and 1s perfectly aligns with this functionality. It is the foundation for representing all digital data - numbers, text, images, audio, video, and more.
The other systems come in handy for specific purposes. Octal acts as a shorthand for binary, making it easier to work with long strings of 0s and 1s. Hexadecimal, with its compact nature, allows for efficient storage and manipulation of data. I found it fascinating how these seemingly abstract concepts power the automation we take for granted. Every click, swipe, or search query involves the underlying conversion between human-readable commands and the language of computers. Understanding number systems unlocks a deeper appreciation for the complex processes happening behind the scenes. It is emphasized that each system has its strengths. Decimal continues to be the dominant system for everyday calculations, while binary forms the core of digital data. Octal and hexadecimal offer efficiency and convenience in specific computing contexts. Mastering these systems equips us, computer science students, to better understand the technology we use and potentially build upon it in the future.
References
Awati, R. (2022, June 20). What is hexadecimal numbering?. WhatIs. https://www.techtarget.com/whatis/definition/hexadecimal
Bansal, R., Banerjee, S., & Goyal Brothers Prakashan. (2017). My book of computer studies (S. Goel, Ed.). Goyal Brothers Prakashan.
Brioli, D. (2023, November 21). Binary Number System | Definition, Application & Examples. Study.com. https://study.com/academy/lesson/binary-number-system-application-advantages.html
Britannica, T. Editors of Encyclopaedia (2024, July 12). decimal system. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/decimal
BYJU’S. (n.d.). Number system (definition, types, conversion & examples) . BYJUS. https://byjus.com/maths/number-system/
Club Z! Tutoring. (n.d.). Decimal number system: Definitions and examples - club Z! tutoring. Decimal Number System: Definitions and Examples. https://clubztutoring.com/ed-resources/math/decimal-number-system-definitions-examples-6-7-8/
Cuemath. (n.d.). Decimal number system - definition, conversion, examples, faqs. https://www.cuemath.com/numbers/decimal-number-system/
Dimitrov, V., Jullien, G., & Muscedere, R. (2017). Multiple-base number system: Theory and applications. CRC Press.
Dixit, J. B. (2005). Fundamentals of computing. Laxmi Publications Pvt Limited.
Encyclopedia.com. (n.d.). Binary Number System. https://www.encyclopedia.com/computing/news-wires-white-papers-and-books/binary-number-system
GeeksforGeeks. (2020, April 16). Decimal number system. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/decimal-number-system/
Kneusel, R. T. (2015). Numbers and computers. Springer International Publishing.
Number system. Number System - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics. (n.d.). https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/mathematics/number-system
Smith, D., & LeVeque, W. (n.d.). numeration systems and numbers. Encyclopædia Britannica. https://kids.britannica.com/scholars/article/numerals-and-numeral-systems/345278
Wahed, A. (2022). Number systems and their operations: Mathematics. ShaShwat Publication.